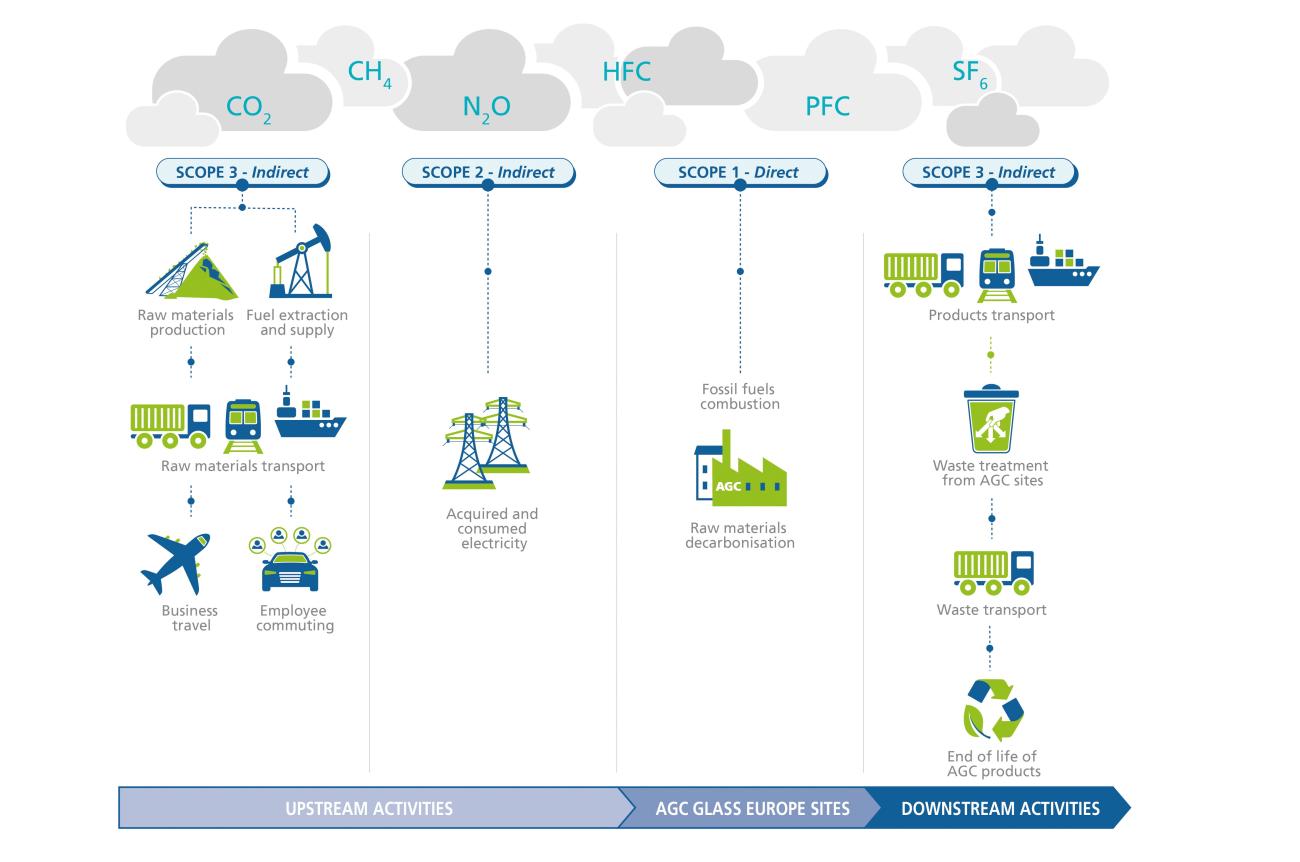
As part of AGC Glass Europe’s strategy and its environmental target for 2030, the carbon footprint is assessed on a yearly basis. Relevant internal data is selected in order to reflect, to a major extent, the real GHG inventories within the company. This allows to track AGC’s emissions over time and to assess the company’s performance in terms of CO2 emissions. This methodology is used as a monitoring framework to draw up our dedicated action plans to overcome our impact on climate change in the short and medium terms. Furthermore, this assessment brings quantified answers and provides customers with a clear view of our corporate impacts.
In 2023, AGC activities in Russia have been sold, to be compliant with GHG protocol rules, the GHG emissions of those activities have been removed from our 2019 baseline and are not considered for our Net Zero trajectory.
According to GHG calculations, it is estimated that in 2024 the Carbon Footprint of AGC Glass Europe (AGEU) was 2.6 million tonnes of CO2 eq*.
(*) The GHG results use the Market-based scenario for Scope 2 calculations. Results include Automotive and Architectural division – AGC sites in 19 countries: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Kazakhstan, Morocco, The Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, and the United Kingdom.
Results show that the main CO2 emissions hotspots are mainly attributed to fuel combustion and raw material decarbonization, raw materials production from our suppliers, and electricity purchased for our production sites. All the mentioned categories represent 80% of the total AGEU CO2 emissions.
Fuel combustion – Scope 1
Fuel combustion represented more than 866 thousand tons of CO2 eq. in 2024. Natural gas consumption in our processes makes this aspect the highest carbon footprint hotspot. To address this challenge, AGC Glass Europe is actively developing technologies that will replace this fuel consumption with hybrid technologies, such as the Volta project.
Electricity consumption - Scope 2
For the first time, AGC Glass Europe is reporting its Scope 2 emissions using the market-based approach, a method that reflects the impact of our efforts to procure renewable energy and low-carbon electricity. This approach goes beyond the traditional location-based method by accounting for the specific energy sources and contractual agreements we have chosen, such as Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) and Guarantees of Origin (GOs).
For AGC Glass Europe, this approach has revealed that our Scope 2 emissions were 292,969 tons of CO2 equivalent in 2024. Thanks to onsite renewable energy projects and the acquisition of Guarantees of Origin, in the reporting year, we have successfully reduced approximately 87 thousand tons of CO2 equivalent in Scope 2 compared to a scenario where these mechanisms were not implemented.
Raw Material decarbonization – Scope 1
In 2024, AGC Glass Europe utilized 730 thousand tons of cullet in its flat glass production processes. The use of cullet minimizes the need for raw materials such as dolomite, sodium carbonate, and limestone, which emit CO2 during high-temperature chemical reactions and decomposition in the melting. To further enhance this effort, AGC Glass Europe launched the Recycle Glass service, which collects and processes glass waste to reintegrate it into flat glass production. This initiative not only supports the circular economy but also maximizes the proportion of cullet used, reinforcing AGC's commitment to sustainable practices and reducing Scope 1 emissions.
AGC Glass Europe's 2024 carbon footprint report highlights its commitment to sustainability through key initiatives, including the procurement of low-carbon electricity sources, the Recycle Glass service, and pioneering projects such as Volta. These actions exemplify AGC Glass Europe's dedication to minimizing emissions and driving progress in its net-zero trajectory.
The impact of these initiatives is reflected in the total quantities of CO2 emissions (Scope 1, 2, and 3) generated due to AGC Europe’s activities, calculated relative to the melted tonnes.
Disclaimer: The total CO2 emissions (Scope 1, 2, and 3) per melted tonne are not intended to serve as a reference for our Product Carbon Footprint. For accurate Product Carbon Footprint data, please refer to our Environmental Product Declarations.
This approach serves to illustrate the gradual improvements achieved through targeted initiatives aimed at enhancing the sustainability of our operations over time.
The company uses the GHG Protocol to account for, report, and mitigate the greenhouse gas emissions occurring in its corporate value chain. Therefore, the results presented every year are intended to be reference values of AGC Glass Europe CO2 emissions, and these may evolve through time. AGC Glass Europe is continuously working on improving its accounting with the purpose of progressing toward its climate goals.